Dermatitis
Dermatitis
- an inflammation of the skin with multiple forms and causes -
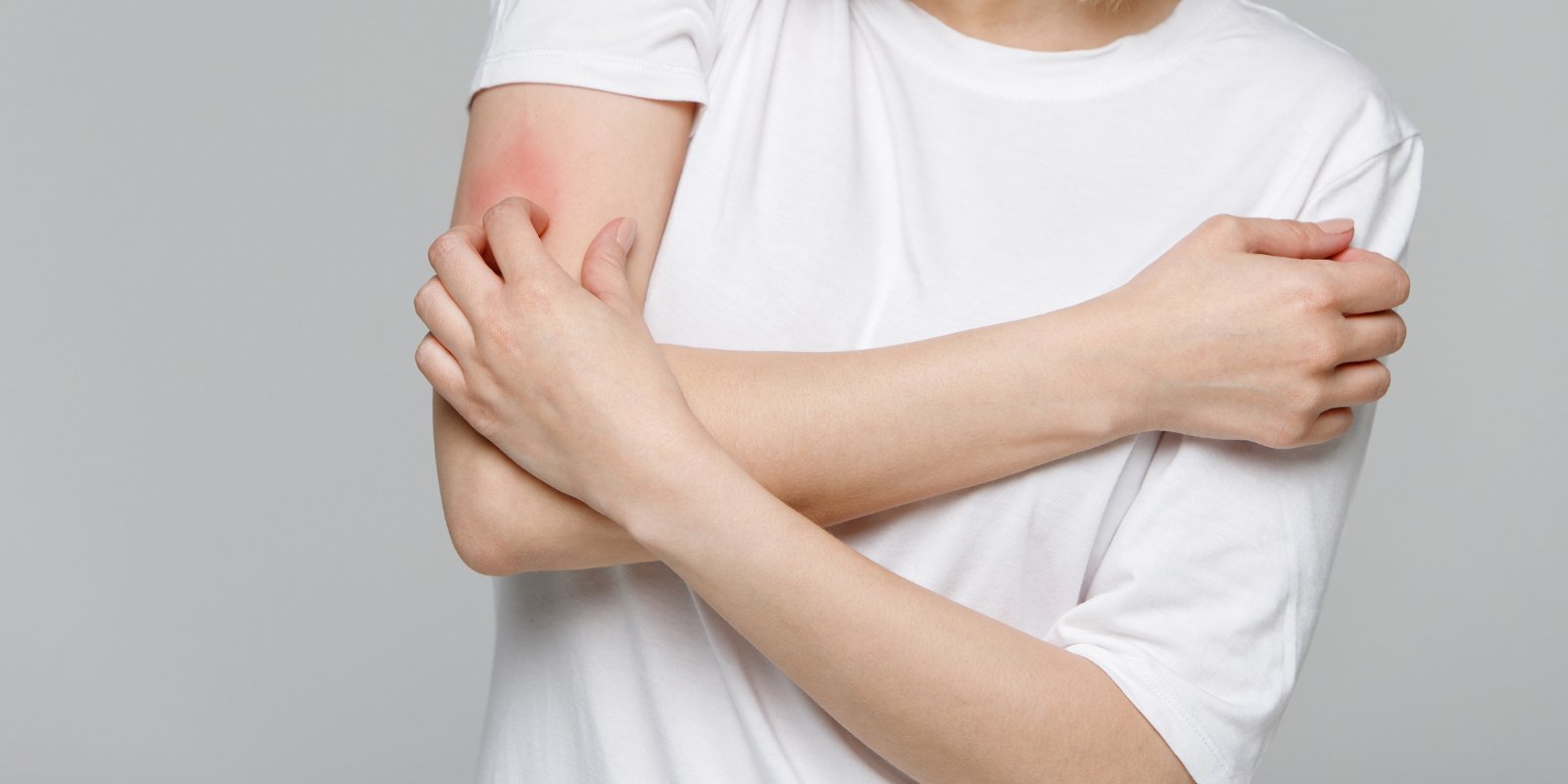
How does dermatitis manifest itself?
- redness and inflammation of the skin
- itching or stinging sensation
- peeling (peeling), dry and cracked skin
- blisters or lesions that may ooze
- the appearance of pigment spots after healing
Types of dermatitis – what differentiates them?
Atopic dermatitis
- It is a chronic form, common in children, but also present in adults.
- Associated with other atopic conditions (asthma, allergic rhinitis).
- Symptoms: dry skin, intense itching, recurring rashes (especially on hands, elbows, knees).
- It requires constant hydration, avoidance of allergens, and topical or systemic treatments.
Contact dermatitis
It is divided into two subtypes:
- tickling – caused by direct contact with aggressive substances (detergents, chemicals, cosmetics).
- Allergic – immune reaction to certain substances (nickel, perfumes, latex).
Both forms require identification and avoidance of the triggering factor, as well as local anti-inflammatory treatment.
Seborrheic dermatitis
- It frequently appears on areas rich in sebaceous glands (scalp, eyebrows, nose area).
- It manifests itself through peeling, redness, and itching.
- Frequently associated with the presence of a fungus (Malassezia).
- Treatments include antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and keratolytic shampoos and creams.
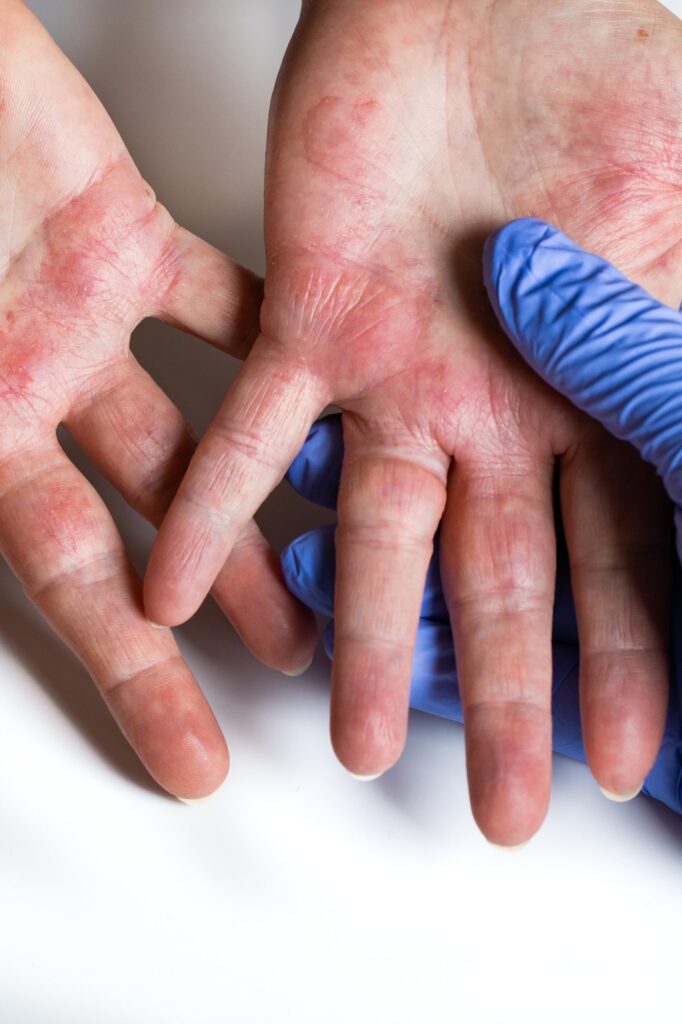
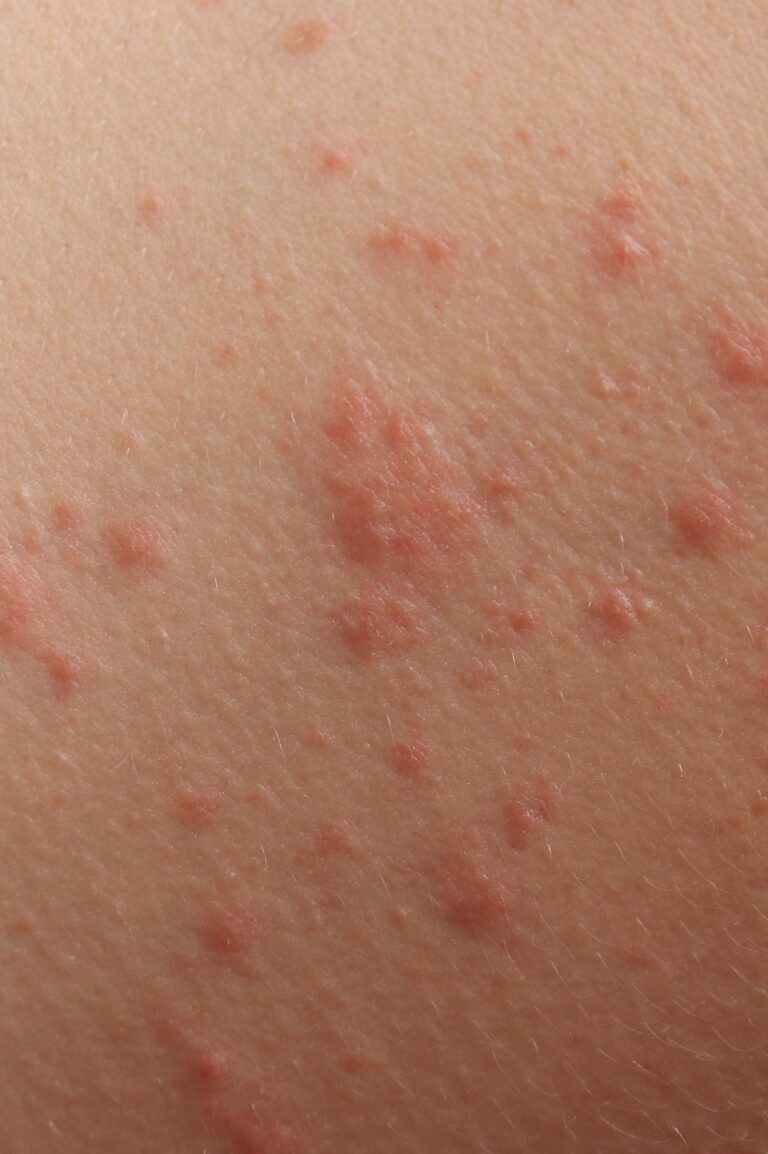
Dermatitis herpetiformis
- A shape rare and severe, related to celiac disease (gluten intolerance).
- It manifests itself through: intensely itchy rashes, grouped blisters, most often on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and scalp.
- Confirmation of the diagnosis requires skin biopsy and tests for celiac disease.
- The treatment involves strict gluten-free diet and, sometimes, specific medication (e.g. dapsone).
Nummular (discoid) dermatitis
- It appears in the form of round, well-defined plates, usually on the limbs.
- It can be confused with other conditions (eczema, psoriasis).
- The cause is not always clear, but it is associated with dry skin, infections, or previous injuries.
- It is treated with emollients and topical corticosteroids.
Perioral dermatitis
- It especially affects young women.
- It manifests itself as red papules around the mouth and nose.
- It may be aggravated by prolonged use of topical corticosteroids.
- Treatment involves stopping irritating products and administering local or systemic antibiotics.
Therapeutic solutions
Topical substances recommended for each type of dermatitis
The treatment of dermatitis is mainly based on correct topical care, adapted to the type of lesion and the sensitivity of the skin. In many cases, the use of mild, restorative, soothing and, if necessary, anti-infective active substances is sufficient to control the condition.
Atopic dermatitis
Treat gently – the focus is on intense hydration, soothing itching, and restoring the skin barrier.
Recommended topical substances:
- allantoin – regenerating, mildly healing, soothing.
- Panthenol (provitamin B5) – repairing, emollient.
- Urea 2–5% – moisturizing and keratoplastic (in low concentrations).
- Aloe vera – soothing, anti-irritant, suitable for sensitive skin.
- Topical antihistamines – to reduce itching (e.g. diphenhydramine, promethazine, etc.).
- Ceramides, hyaluronic acid – restore the skin barrier.
- Topical corticosteroids only in acute flare-ups and for the short term.
Contact dermatitis (irritant or allergic)
The objective is to calm inflammation, restore the epidermis, and protect the skin from further irritation.
Recommended topical substances:
- Zinc oxide – soothing, slightly astringent, protective.
- Dexpanthenol – epithelial regeneration.
- Aloe vera – soothing, anti-irritant, suitable for sensitive skin.
- allantoin – reduces redness and promotes healing.
- Zinc PCA – regulates sebum secretion, mild antibacterial action.
- Glycerin and urea 2–5% – for hydration.
- Topical corticosteroids are only used in moderate-severe forms and for a short duration
Seborrheic dermatitis
Controlling inflammation and fungal proliferation (Malassezia) is important.
Recommended topical substances:
- Ketoconazole 2% – first-line antifungal.
- Ciclopirox olamine – antifungal and anti-inflammatory.
- Zinc pyrithione – antifungal and soothing.
- Salicylic acid 2% – gentle keratolytic, reduces scales.
- Precipitated sulfur 2–5% – regulates sebum secretion.
- PANTHENOL – moisturizing adjuvant.
- Zinc oxide – soothing, anti-irritant.
- Carbon Black – reduce pruritul și usucă leziunile.
- Aloe vera – calming, natural anti-inflammatory effect.
- Topical antihistamines – for intense itching.
Nummular (discoid) dermatitis
Lesions tend to be chronic and may require keratolytic substances + deep hydration.
Recommended topical substances:
- Urea 5–10% – emollient + mild keratolytic.
- allantoin – soothing and healing.
- Glycerin, Vaseline – to restore the lipid barrier.
- Salicylic acid 2% – in hyperkeratotic plaques.
- Topical antibiotics (in case of superinfection): fusidic acid, mupirocin, neomycin, chloramphenicol, etc.
- Topical corticosteroids only in obvious inflammatory phases, for a limited period.
Perioral dermatitis
Very sensitive to corticosteroids – these should be discontinued completely. Treatment focuses on antibacterials and restoring the skin barrier.
Recommended topical substances:
- Metronidazole 0.75–1% – recommended topical antibacterial.
- Clindamycin 1% – antibacterial alternative.
- Niacinamide (vitamin B3) – anti-inflammatory, reduces redness.
- Azelaic acid – anti-inflammatory, well tolerated.
- Glycerol, panthenol, hyaluronic acid – for hydration and soothing.
Master treatments
personalized for your skin
- are formulated specifically for the type and location of dermatitis
- reduce the risk of side effects through optimized dosing
- personalization based on symptoms and patient compliance.









